专业制造商
质量保证
及时交货
贴心售后
COMPANY INTRODUCTION
专业的流体解决方案提供商
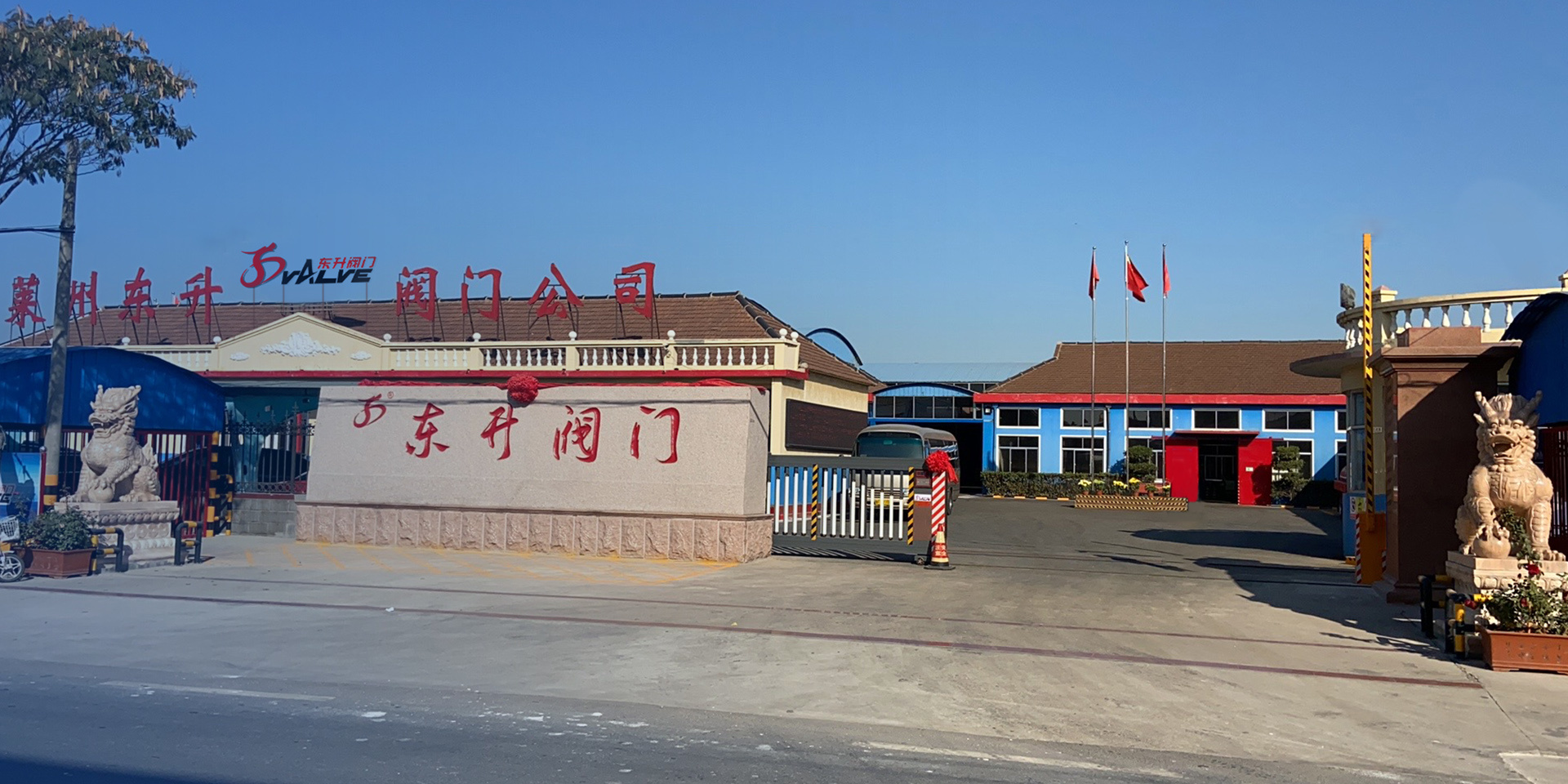
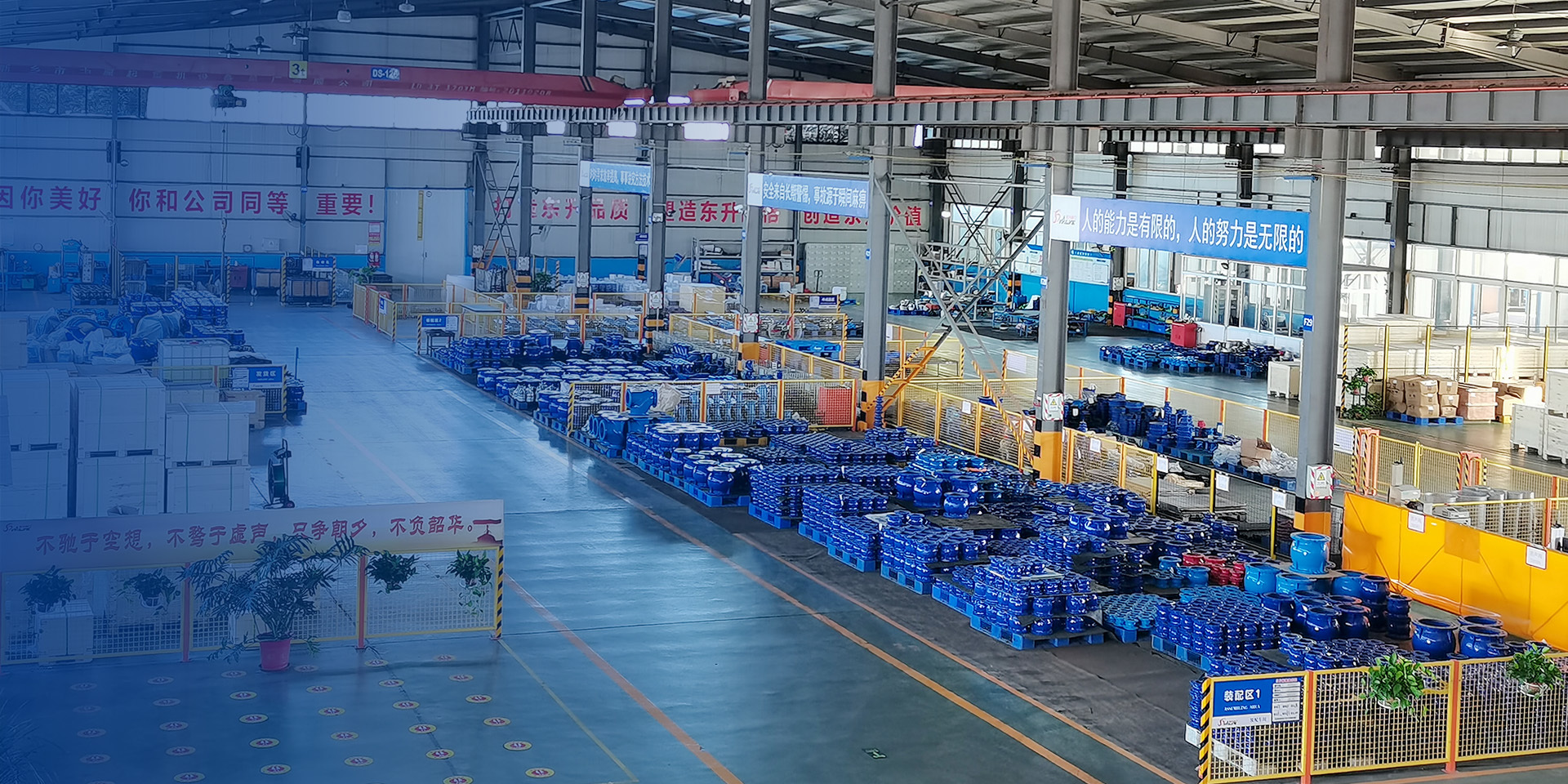
莱州市东升阀门有限公司(以下简称公司)成立于2002年,位于齐鲁文化底蕴深厚的山东省莱州市,是一家集制造、销售和设计研发于一体的工贸出口型企业。
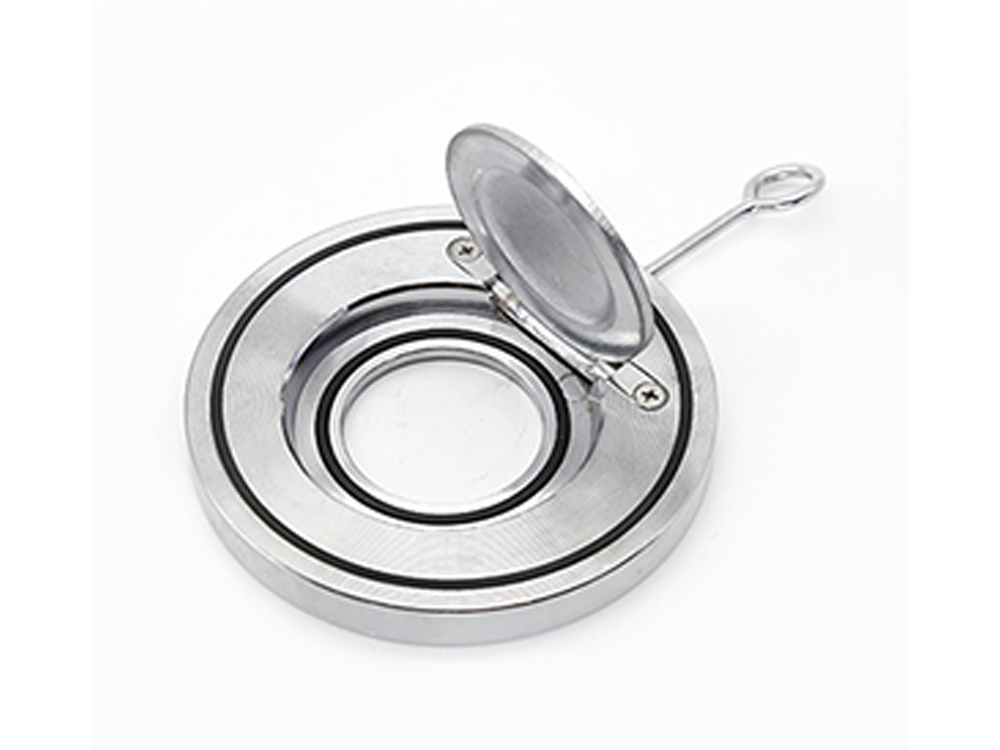
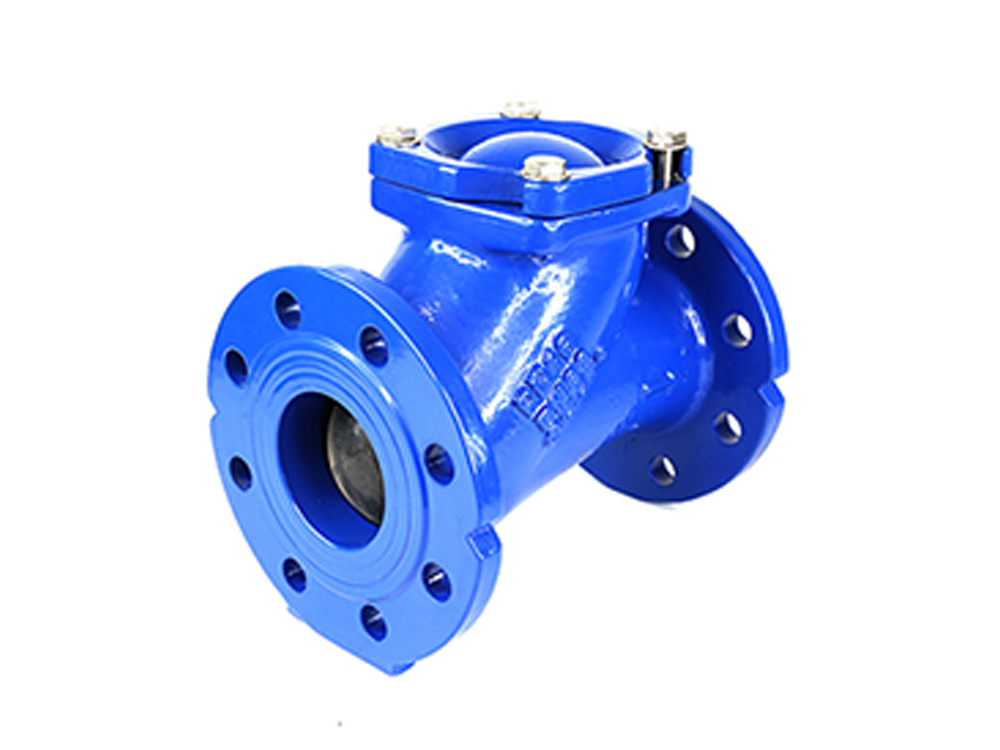
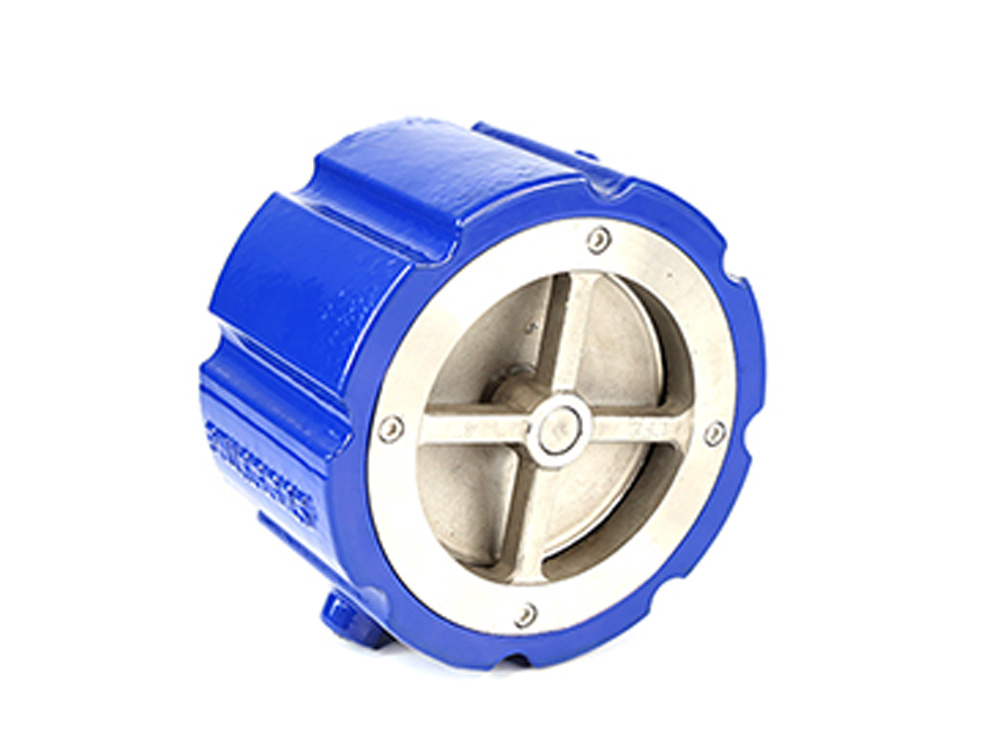
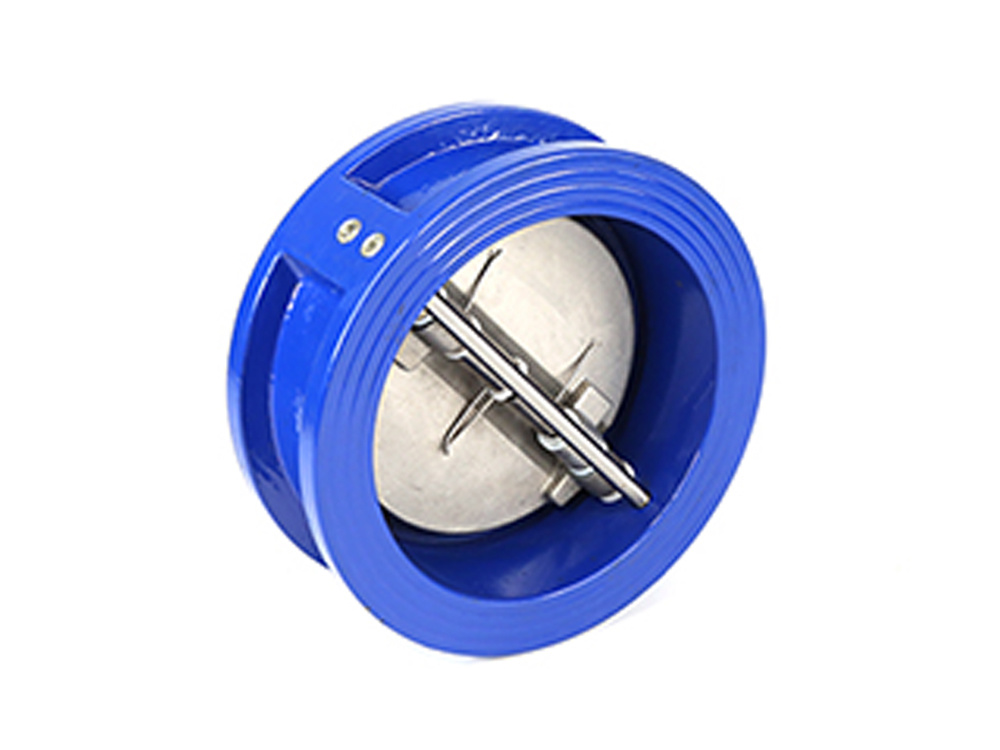
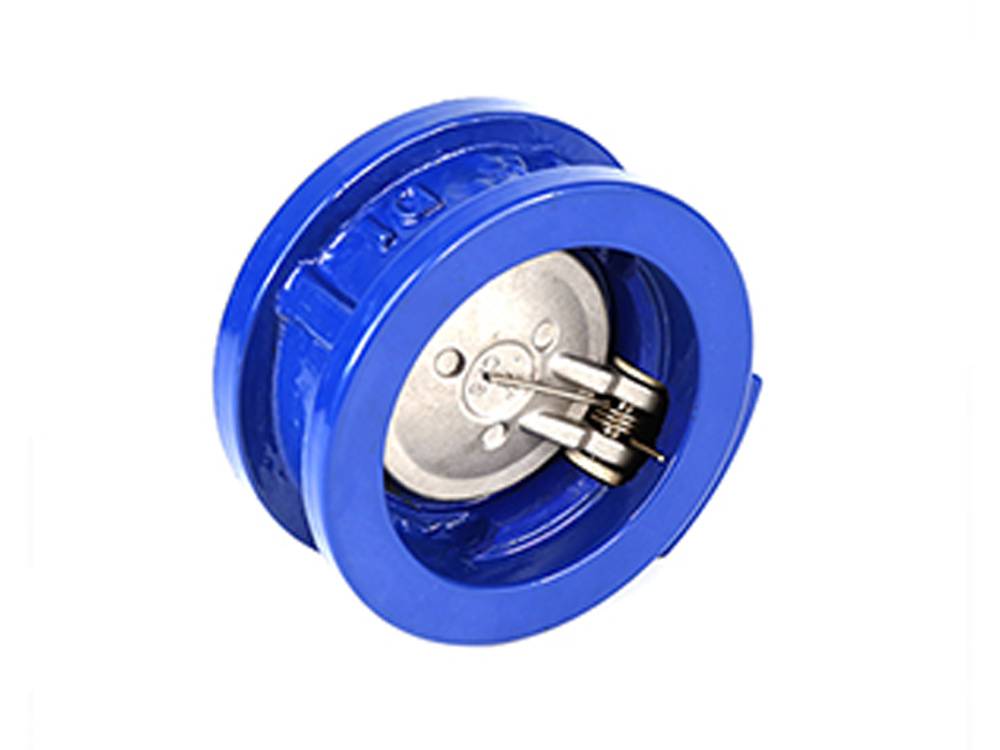
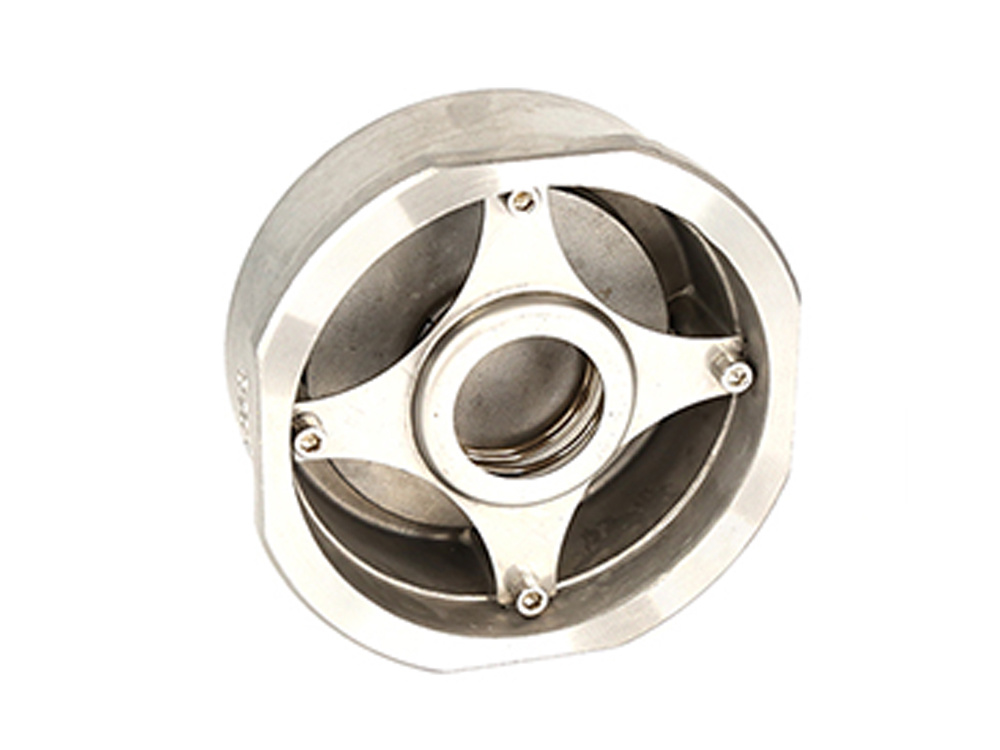
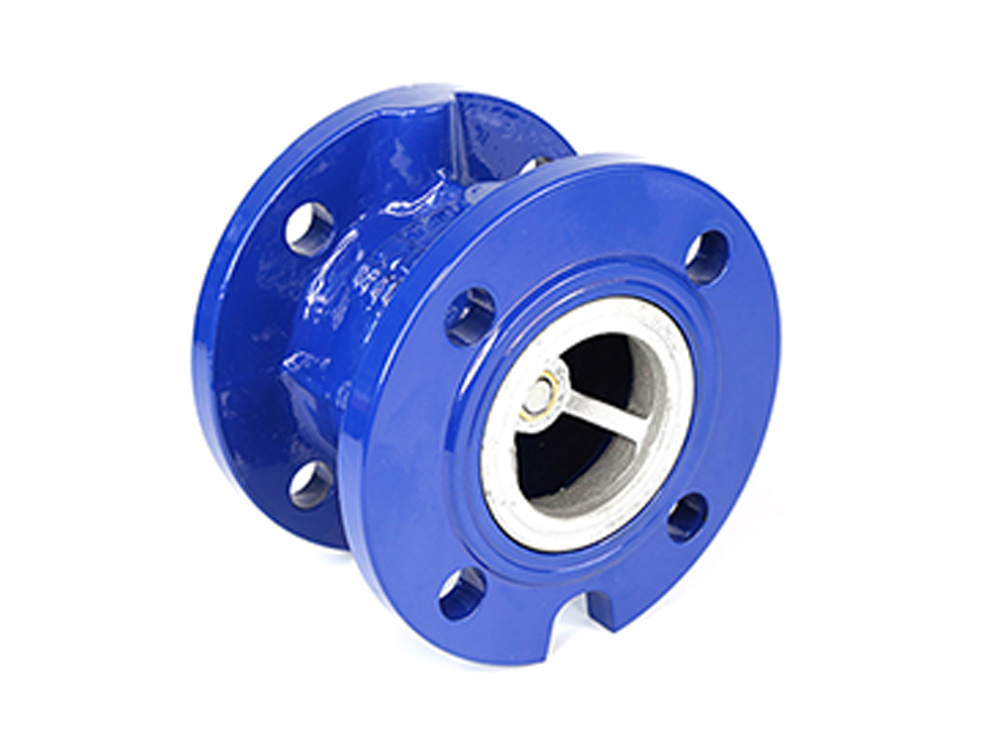
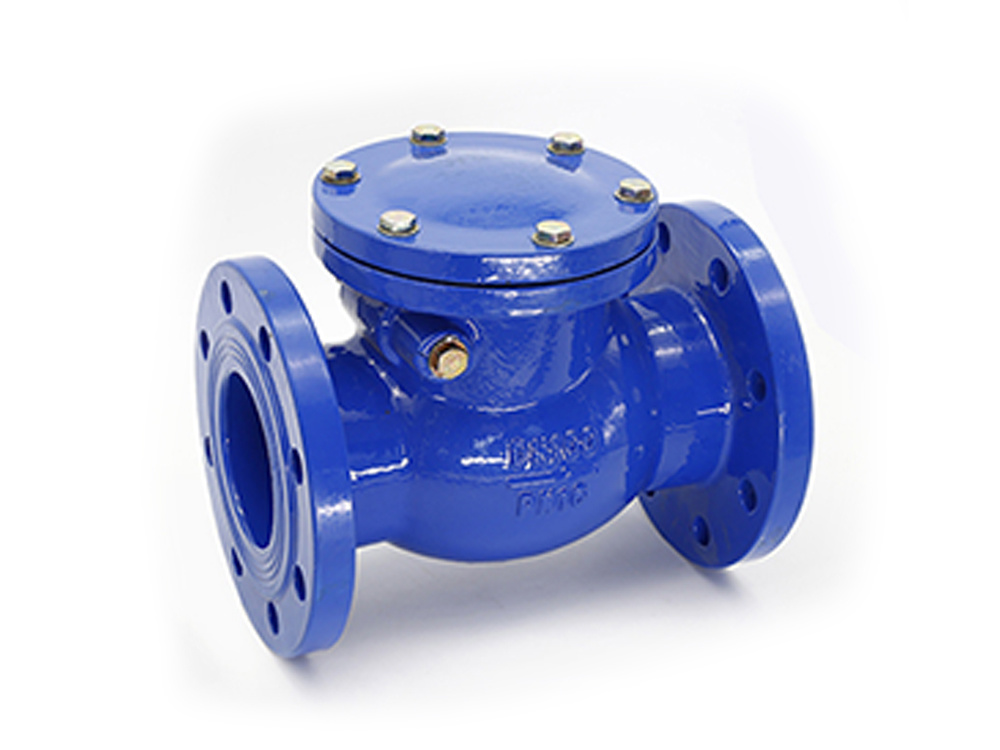
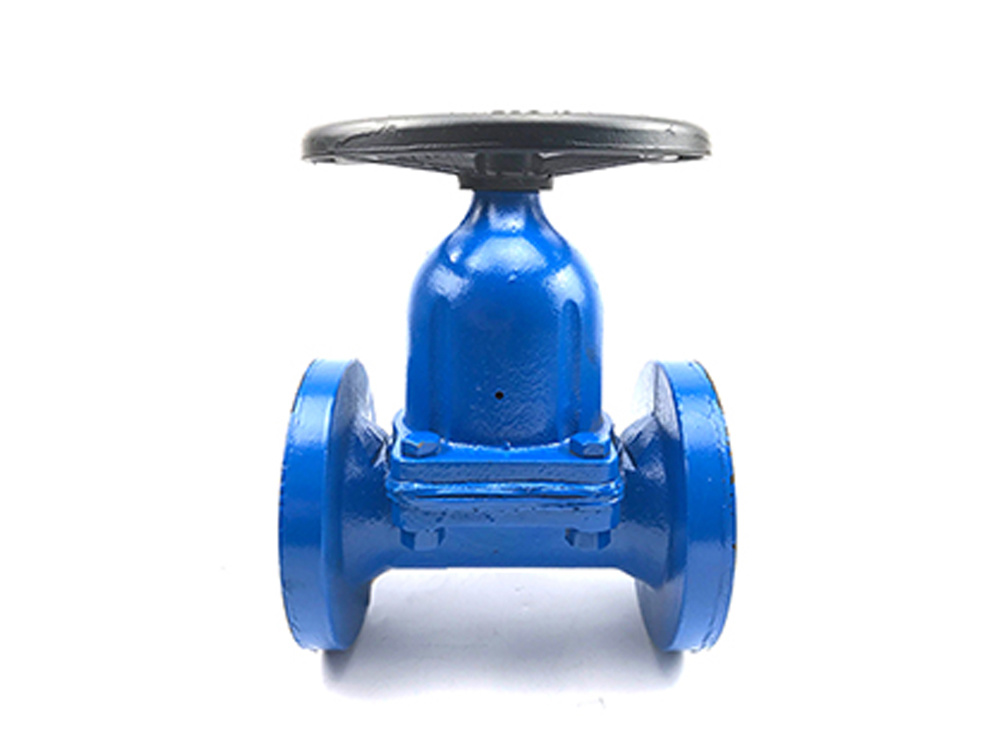
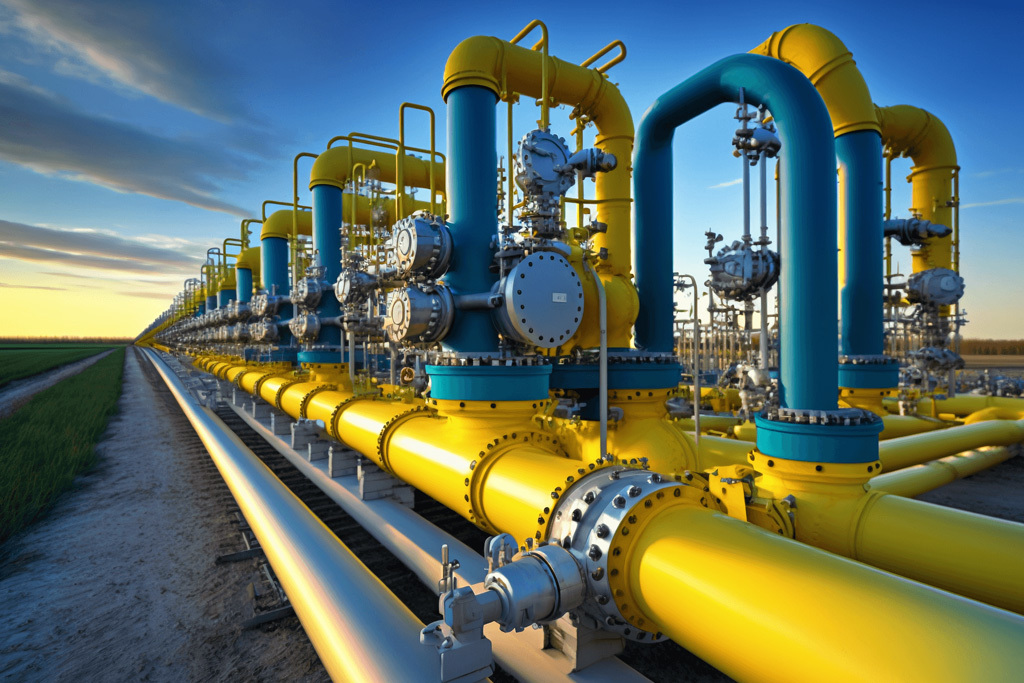
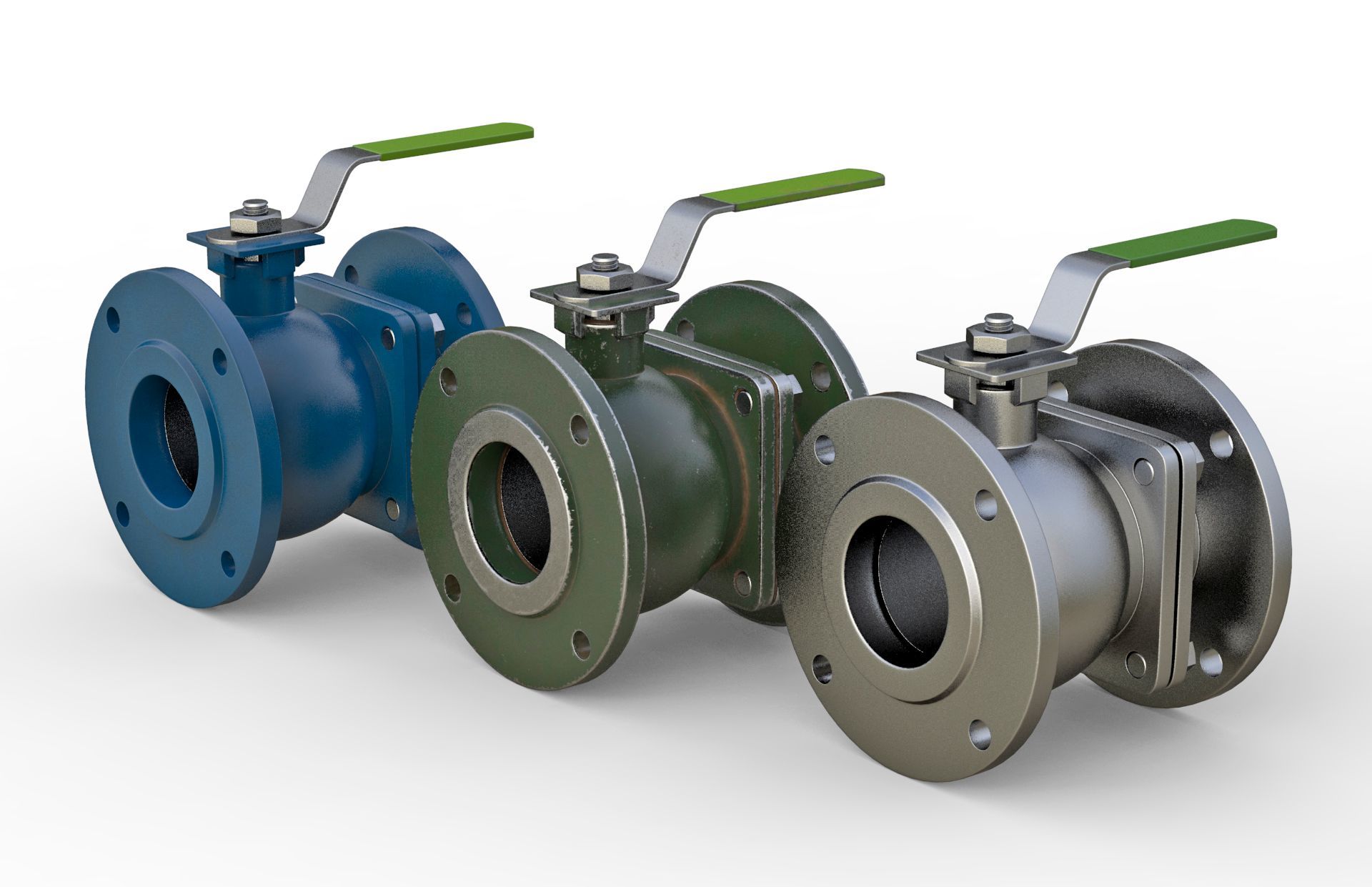
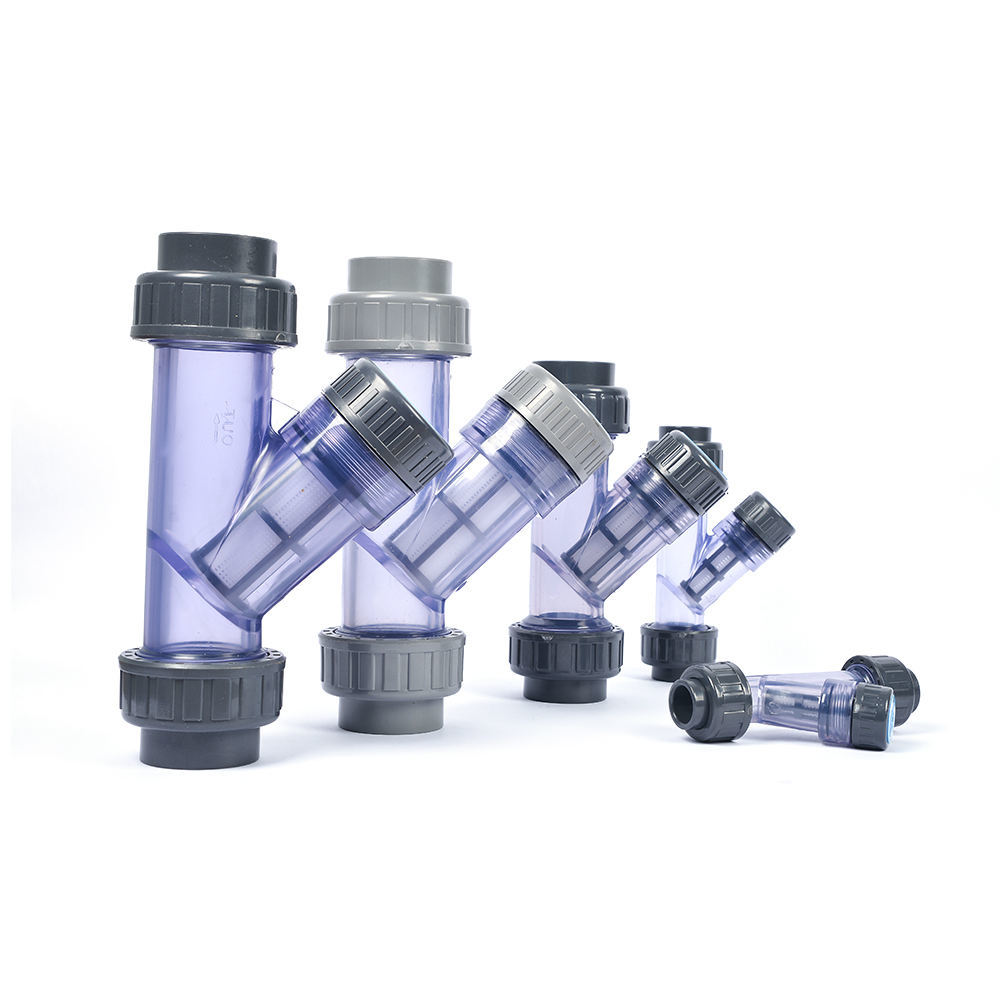
公司主要制造止回阀、隔膜阀、球阀和蝶阀等产品,产品广泛应用于石油、化工、矿业及供排水、净化水、蒸汽、流体食品、酸碱溶液等管路设备系统,以高端阀门产品为重点,主销欧美市场。
20
+
产品型号及规格
500
+
产品型号及规格
70
+
产品销售国家和地区
NEWS INFORMATION
聚焦资讯新闻
GET IN TOUCH WITH US!
有问题?联系我们